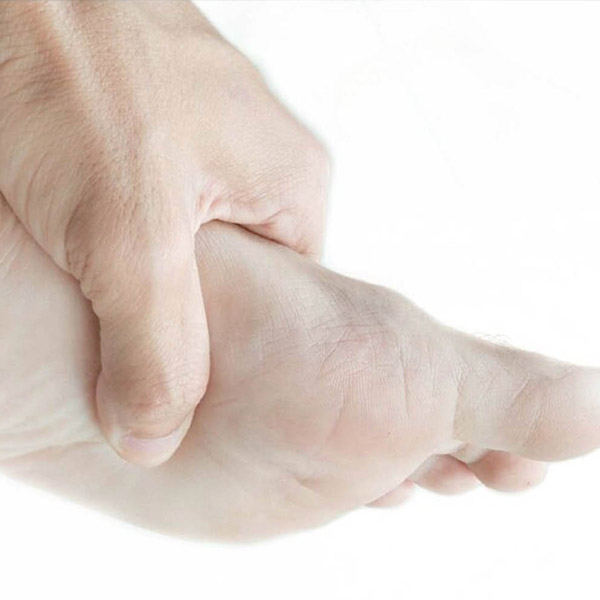
The big toe also called first metatarsolphalangeal joint (MTP) joint osteoarthritis (OA) is a common and painful problem that causes significant disability. In a recent Australian /UK study 7.8% of those over 50 years of age suffered from symptomatic pain in first MTP joint. People with this condition also experienced difficulties performing functional weight- bearing activities and worse quality of life compared with those without the condition.
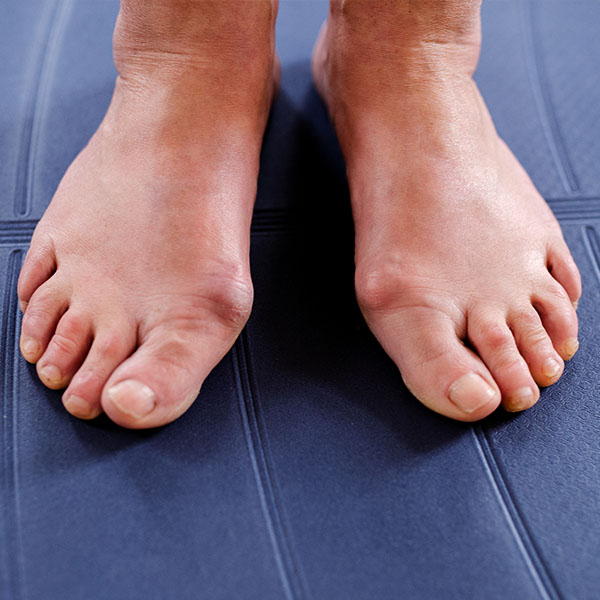
A Bunion (Hallux Valgus) is a lateral deviation of the Big Toe at the First Metatarsal joint. They are not growths as is the common misconception; however, do become more prominent as the deformity progresses.
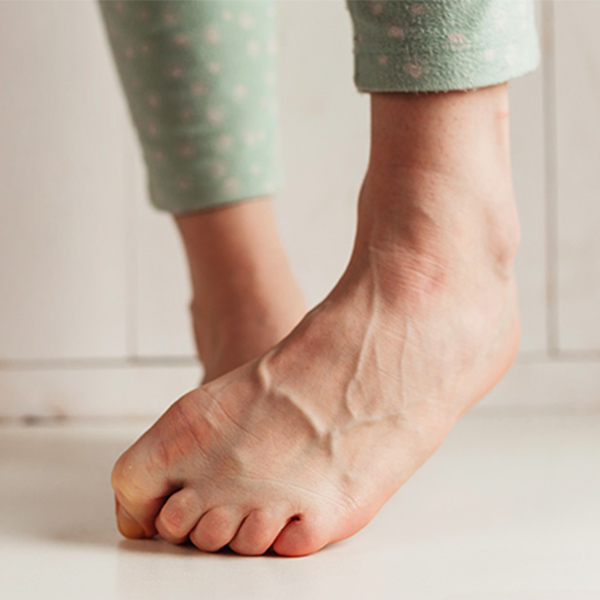

Bent toes in an odd position known as Toe Clawing, are generally due to tight muscles underneath the foot. Tight or ill-fitting shoes can cause the muscles of the foot to become out of balance.
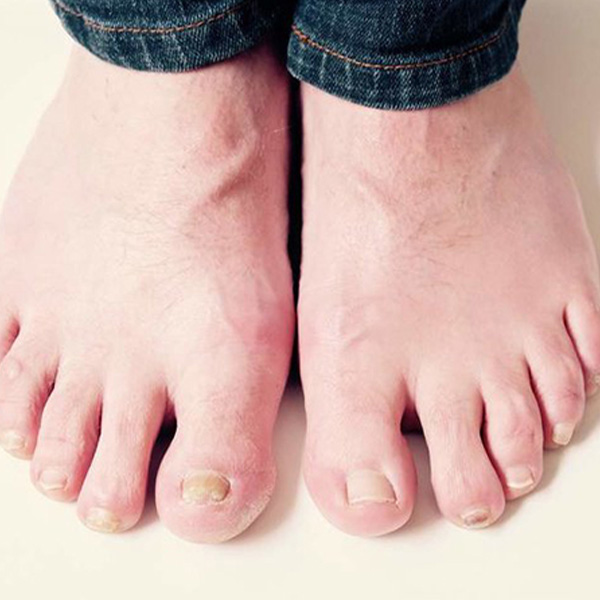
Ingrown toenails occur when a nail edge pierces or presses into the skin. The skin can the become tender, swollen and even infected.
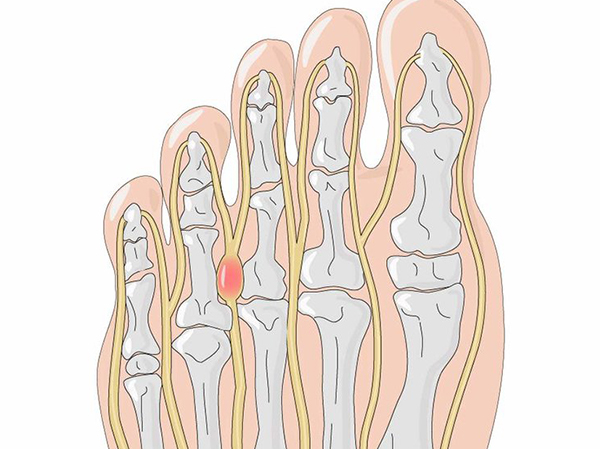
Morton’s Interdigital neuroma is a swelling or irritation of the nerve usually between the third and fourth metatarsals of the foot. It can often be associated with intermetatarsal bursitis, which may also cause compression of the nerve.
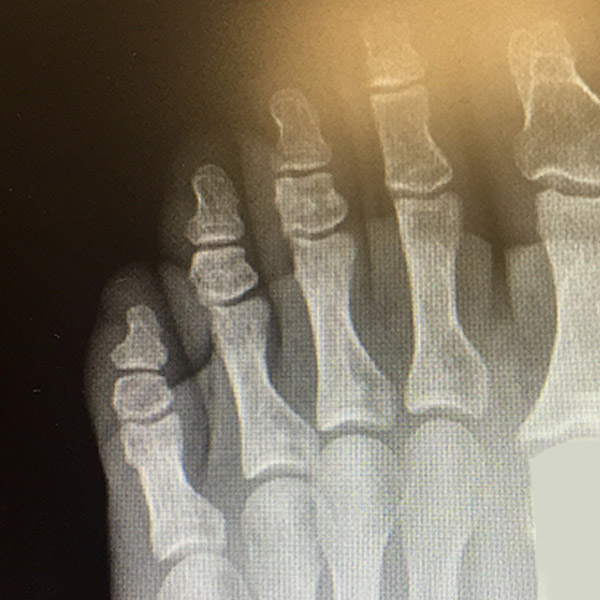
A ‘Stress Fracture’ is a micro fracture or a small crack in a bone due to repetitive loading, often by overuse. The applied load is less than that required for a single fracture. They are most common in weight bearing bones of the foot and leg and resulting from impact forces, or the action of muscles pulling across the bone.

The Plantar Fascia is a thick band of connective tissue that supports the arch and provides dynamic shock absorption.
What Is Plantar Fasciitis?
Plantar Fasciitis is an overuse condition where the collagen of the plantar fascia is damaged. This can occur in the arch or heel of the foot.
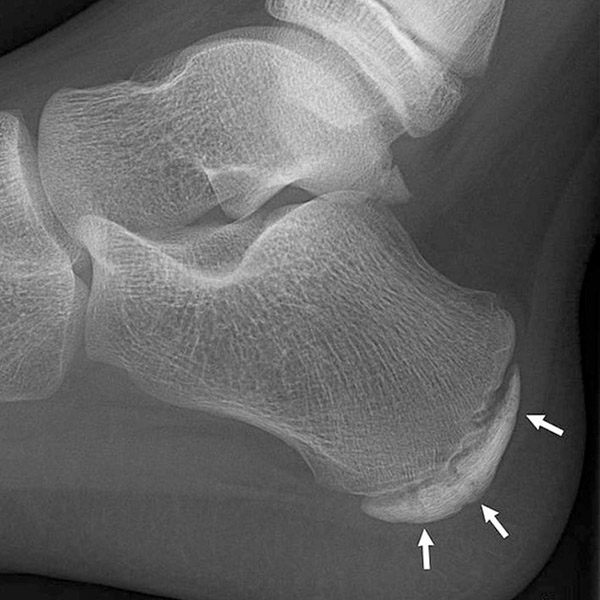
Is your child complaining of sore heels after sport?
Pain in the heel and ankle are very common complaints of growing, active children. As we want to keep them active, it is important to have these problems assessed and not just dismiss them as growing pains.
One of the most common causes of the heel pain is sever’s disease, or traction calcaneal apophysitis. This problem usually involves an inflammation of the growth plate in the heel bone called the calcaneus. The average age is usually between 8-14 years of age.
Ankle Sprains are a common sporting and mishap injury. Usually the injury involves stretching or tearing the outside ligaments of the joint which will happen when the ankle moves inwards. Occasionally the inside ligaments can be injured when impact is high or when the ankle is moved forcefully outwards.

Copy required
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
Peroneal Tendinopathy is the most common cause of pain on the outside of the ankle resulting from overuse. There are two Peronel Tendons that cross the lateral ankle joint to insert to the outside of the foot and under the big toe joint. Damage to the tendons may be the result of acute injury (ankle sprain) by overuse or lateral instability of the ankle.
The Tibialis Posterior Tendon functions to control or decelerate foot pronation (rolling in). The tendons are dynamic stabilisers of the rearfoot and help support the arches of our feet. Tibialis Posterior Tendinopathy is the most accurate term to describe overuse conditions of the tendon characterised by tissue damage.

Patello-Femoral pain is a medical term used to describe all pain at the back of the patella (knee cap) where it articulates with the femur (thigh bone). It is one of the most common knee pain complaints in both active sports people and those who have experienced more wear and tear. The average person walks 150,000 kms plus in a lifetime.

Shin splints or shin pain can be caused by injuries to the muscle along the shin, stress fractures and compartment syndrome.
Shin pain is a common injury that affects athletes who engage in running sports and other activities such as tennis, golf and walking.
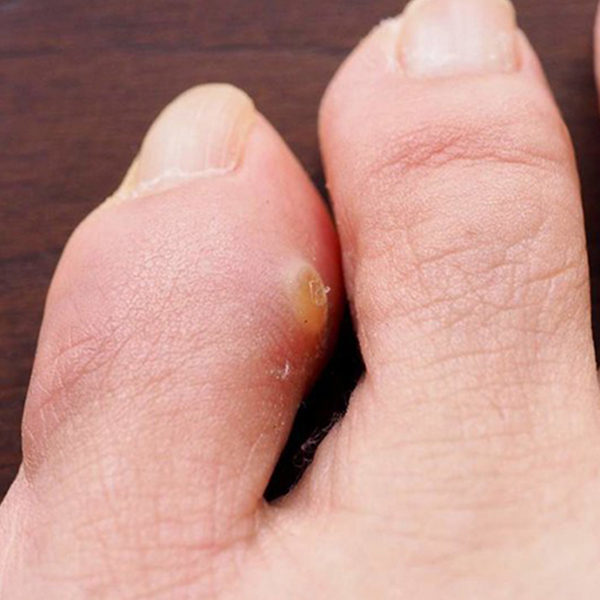
A corn is a small circular thickened lesion in the skin of the foot.
Corns can also occur under the feet due to abnormal alignment within the foot posture.

It may be difficult to imagine when looking at a newborn baby that they have around 300 bones and those bones are growing and changing every day. Adults on the other hand have 206 bones.
The process of bone development is called ossification. At birth many of the bones are made entirely of cartilage, a type of connective issue that is tough and flexible. As a baby grows into childhood, much of that cartilage will be replaced by actual bone. As the bones grow, they fuse together and this is why the actual number of bones decrease.
By 18 years of age most of the bones are fully formed but up to that age, children’s feet go through many changes.
As toddlers, children are encouraged to stand and walk at their own pace. They don’t really require footwear indoors and on soft surfaces as it helps promote strong muscles within the feet and legs.
Children go through normal stages of walking with their toes pointing out with knees bent, then toes pointing inwards. These are normal at different ages but if a child is tripping a lot, crying and rubbing legs or complaining of pain, it is a good idea to have your Podiatrist assess them.
As young children’s feet are soft and pliable, prone to damage from abnormal pressures, correct shoe fitting is very important. Children’s feet will grow 2 shoe sizes a year up to the age of four and roughly 1 shoe size a year from then on.
Check small children’s feet at least 1-3 months up to the age of 3 years and then every 4 months up to the age of 5 and then every 6 months from 5 years of age.
Heel pain can also occur in growing children between the ages of 8-13 as they start to play more sports. If pain is limiting their activity, it is a good idea to have this investigated by Rich River Podiatry. Your Podiatrist can let you know if the heel pain is part of the growing process or injury related and suggest a treatment plan either way.
Children and teenager’s feet are more susceptible to Warts as their immune systems are still developing. If a Wart is painful or spreading quickly it is highly recommended to have them assessed. They are highly contagious, and it is a good idea to wear thongs in the shower otherwise the rest of the family and friends may contract them.